Collateral assignment of life insurance is a strategic financial tool that allows individuals to leverage their life insurance policies as collateral for loans. This practice provides lenders with assurance that their funds are secure, enabling borrowers to access loans more easily and potentially at better terms.
Understanding the concept of collateral assignment of life insurance is crucial for those seeking to utilize this method in financial transactions.
What is a Collateral Assignment of Life Insurance?
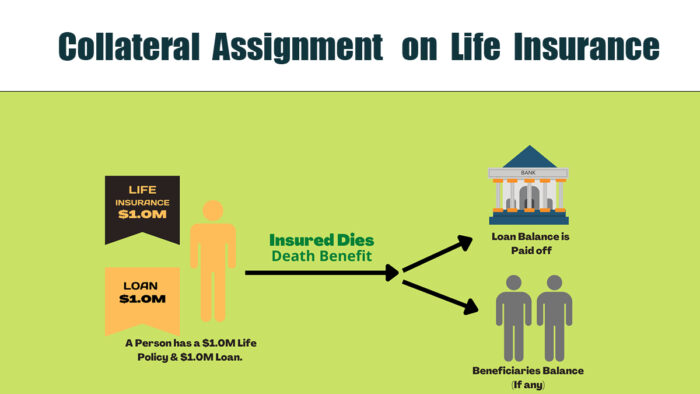
Collateral assignment of life insurance involves designating a lender as the assignee of a life insurance policy’s death benefit to secure a loan. This means that in the event of default or the borrower’s death before the loan is repaid, the lender has the right to claim a portion or all of the death benefit to cover the outstanding loan amount.
Unlike naming the lender as a beneficiary, a collateral assignment allows borrowers to specify the exact amount owed to the lender, ensuring that any remaining benefit goes to their chosen beneficiaries. This arrangement typically requires the borrower to maintain the policy and continue premium payments until the loan is fully repaid.
It is essential to note that a collateral assignment of life insurance is irrevocable, providing lenders with a level of security in loan transactions.
How a Collateral Assignment of Life Insurance Works
Collateral assignment of life insurance works by designating a lender as the assignee of a life insurance policy’s death benefit to secure a loan. The borrower, who must be the policy owner, can use either term or whole life insurance for this purpose.
If the borrower defaults or passes away before repaying the loan, the lender can claim the outstanding balance from the death benefit. Notably, the lender is only entitled to the loan balance, and any remaining benefit goes to the policy’s beneficiaries. The borrower must maintain the policy and continue premium payments until the loan is repaid.
Once the loan is fully repaid, the collateral assignment is removed, and the lender no longer has a claim on the death benefit. This process ensures that the lender is repaid what is owed while safeguarding the interests of the borrower’s beneficiaries.
Example of Collateral Assignment of Life Insurance
For example, let’s say a small business owner needs a $50,000 loan to expand their floral shop. To secure the loan, the bank requires collateral, and the business owner decides to use their life insurance policy for this purpose.
In this case, if the business owner were to pass away before repaying the loan, the lender would have a claim to the outstanding balance from the death benefit of the life insurance policy. However, any remaining funds from the death benefit would still go to the policy’s designated beneficiaries.
This example illustrates how a collateral assignment of life insurance can be utilized in a business context to secure financing while protecting the interests of both the borrower and their beneficiaries.
Alternatives to Collateral Assignment of Life Insurance
- Secured Loans with Other Assets: Borrowers can opt for secured loans using assets like real estate, vehicles, or investments as collateral instead of a life insurance policy. This method allows borrowers to secure loans without affecting their life insurance benefits.
- Unsecured Loans: Borrowers can explore unsecured loans that do not require collateral. While these loans may have higher interest rates, they eliminate the need to use life insurance as collateral, providing more flexibility in financial transactions.
- Co-Signers: Another alternative is to involve a co-signer with a strong credit history to guarantee the loan. This method can help borrowers secure loans without pledging their life insurance policies.
- Personal Guarantees: Borrowers can offer personal guarantees by pledging personal assets or agreeing to repay the loan personally in case of default. This approach can be an alternative to using life insurance as collateral.
- Lines of Credit: Borrowers can consider lines of credit where they can access funds up to a certain limit without requiring collateral. This option provides flexibility for borrowing without risking life insurance benefits.
These alternatives offer borrowers various options to secure loans without using their life insurance policies as collateral, providing more choices in financial planning and decision-making.
What Are the Benefits of Collateral Assignment of Life Insurance?
Collateral assignment of life insurance offers several benefits for borrowers seeking to secure loans. This strategy allows individuals to use their life insurance policies as collateral, providing a secure way to access financing without risking personal assets like homes or vehicles.
Additionally, life insurance premiums are often more affordable than the interest rates on unsecured loans, making it a cost-effective option for borrowers. Financial institutions view life insurance as a reliable form of collateral, increasing borrower attractiveness to lenders and improving the chances of loan approval.
Furthermore, collateral assignment ensures that any remaining death benefit not used to repay the loan goes to the policy’s designated beneficiaries, protecting their financial interests. Borrowers also benefit from the flexibility of being able to use different types of life insurance policies, such as term or permanent life insurance, as collateral, allowing them to choose the policy that best fits their needs and loan requirements.
Overall, it provides a secure, affordable, and flexible way for borrowers to access financing while safeguarding the interests of both themselves and their beneficiaries.
Which Types of Life Insurance are Eligible for Collateral Assignment?
The types of life insurance eligible for collateral assignment include both term life insurance and permanent life insurance policies. Term life insurance can be used as collateral, provided that the policy aligns with the size and duration of the loan, with coverage and term length meeting or exceeding the loan’s terms.
On the other hand, lenders often find permanent life insurance policies appealing for collateral assignment due to their cash value component, which provides an added level of reassurance to the lender.
Permanent life insurance policies that accumulate cash value, such as whole life, universal life, variable life, or variable-universal life, are also eligible to be used as collateral, subject to the specific requirements of each financial institution.
It’s essential to discuss these requirements with the lender before purchasing life insurance with the intention of using it as collateral for a loan.
Is the Collateral Assignment of Life Insurance Unchangeable?
Yes, the collateral assignment of life insurance is typically irrevocable, as established by a written agreement between the policyholder and the lender. This agreement prevents the policyholder from altering or revoking the assignment without the lender’s consent.
Once the collateral assignment is in place, it remains binding unless the lender confirms that the debt secured by the assignment has been fully repaid.
This irrevocability ensures that the lender has a secure interest in the life insurance policy as collateral for the loan, providing them with assurance that the outstanding loan amount can be recovered if needed.
What Sets Apart an Assignment From a Collateral Assignment?
An assignment differs from a collateral assignment in that an assignment involves the transfer of ownership rights of an asset to another party, while a collateral assignment is a specific type of assignment where the ownership rights of an asset are transferred as additional security for a loan.
In an assignment, the new owner (assignee) gains full control and ownership of the asset, whereas in a collateral assignment, the ownership rights revert to the original owner (assignor) once the loan is repaid.
The collateral assignment serves as an additional security measure for the lender, ensuring that they have a claim on the asset if the borrower defaults on the loan. This distinction highlights that while both assignments involve the transfer of rights, a collateral assignment specifically functions to secure a debt obligation.
FAQs
What types of life insurance policies can be used for collateral assignment?
Both term life insurance and permanent life insurance policies, such as whole life, universal life, variable life, or variable-universal life, can be used for collateral assignment, subject to specific lender requirements.
What are the benefits of using life insurance as collateral for a loan?
Using life insurance as collateral for a loan offers benefits such as easier access to financing, potentially better loan terms, protection for beneficiaries, and the ability to secure loans without risking other assets like homes or vehicles.
Can I borrow against my life insurance policy without collateral assignment?
Yes, some life insurance policies offer the option to borrow against the cash value of the policy without requiring collateral assignment. This type of loan is typically known as a policy loan and is secured by the cash value of the policy itself.
What happens to the remaining death benefit if I use collateral assignment for a loan?
If you use collateral assignment for a loan and there is a remaining death benefit after the loan is repaid, it goes to the policy’s beneficiaries. The lender is only entitled to the amount needed to cover the outstanding loan balance.
Are there alternatives to collateral assignment for securing loans using life insurance?
Yes, alternatives to collateral assignment include secured loans with other assets, unsecured loans, co-signers, personal guarantees, and lines of credit. Each option has its own advantages and considerations, providing borrowers with flexibility in securing loans using life insurance.


